
Dr. Shekhar Srivastav is the senior orthopaedic consultant & Robotic Knee Replacement Surgeon performing Joint Replacement & Arthroscopic Surgeries of Knee & Shoulder Joints and is HOD of the Orthopedics Department Delhi Institute of Trauma and Orthopaedics (DITO),
Sant Parmanand Hospital. He has a keen interest in management of Knee & Shoulder problems, Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery.
He has performed thousands of Total & Partial Knee Replacement( Primary, Revision & Unicondylar replacement) & Arthroscopic Surgeries ( ACL, Meniscus, Cartilage surgeries). Similarly in Shoulder he’s an expert in performing Shoulder Arthroscopies ( Bankart repair, Rotator Cuff Repair) & Shoulder replacement Surgeries ( Total & Reverse Shoulder Replacements).

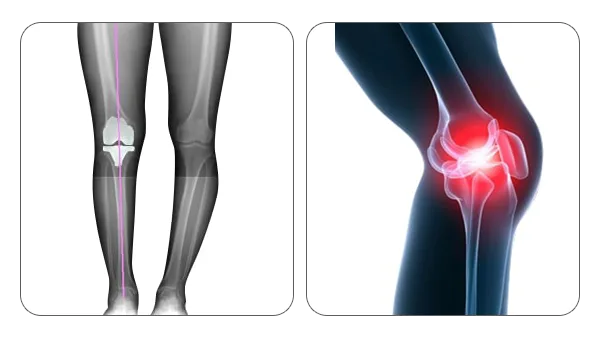
The procedure for a Total knee Replacement (TKR) has advanced greatly with the development of new materials and the increasing understanding of the knee joint biomechanics. An accurate alignment of the component and soft tissue balancing has been cited as the essential for the success of Total knee Joint Replacement (TKR). Although mechanical alignment guides have been designed to improve alignment accuracy, there are several fundamental limitations of this technology that will inhibit additional improvements.
Traditional knee replacement Surgery
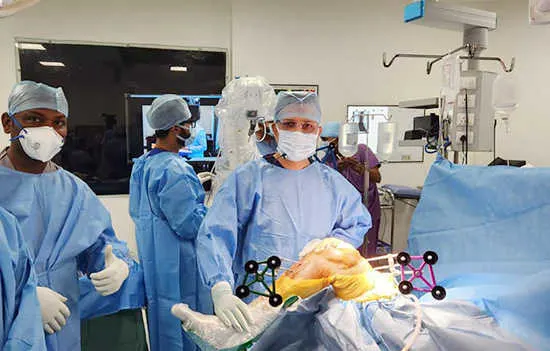
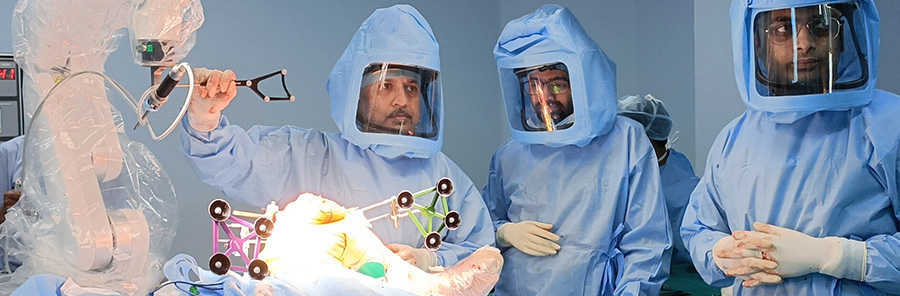
Robotic Knee Replacement Surgery
There are limits on improving the alignment accuracy using a conventional total knee replacement. Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) was introduced to overcome the difficulties and errors. Computer-assisted total knee Replacement has gained increasing acceptance among orthopedic surgeons as a technique to improve surgical precision and patient outcomes.
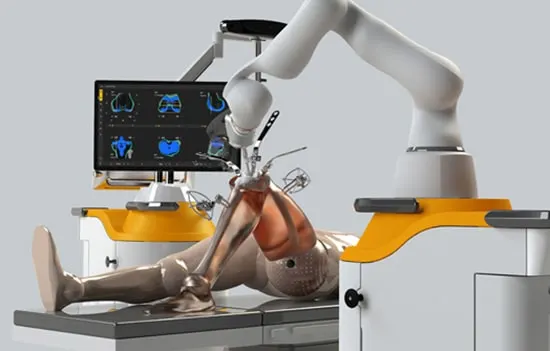
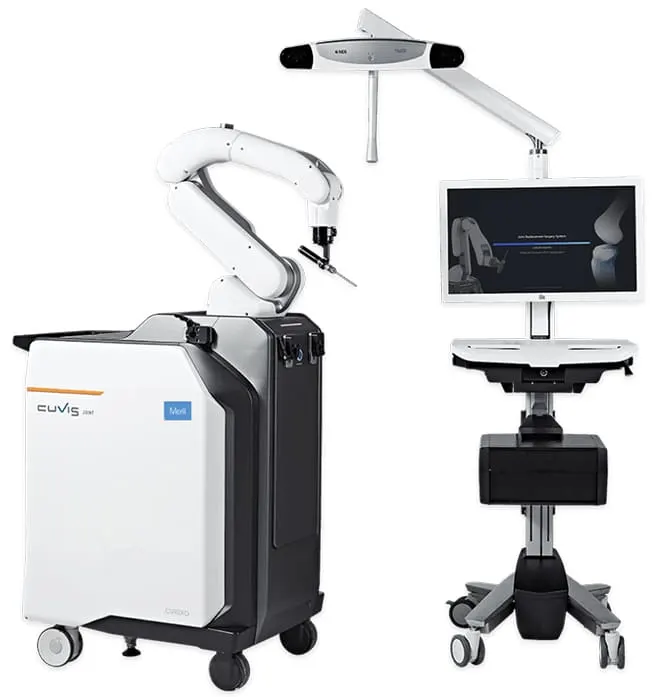
The Joint Replacement surgical robotic system is the most advanced surgical equipment capable of 3D pre-planning, virtual surgery and precise cutting to provide accurate and precise surgery results.
With the advent of Robotic technology in TKR surgeries the limitations have been drastically mitigated with 3D CT pre-planning, Accuracy and predictability in surgical outcome.
In knee replacement surgery, the arthritic portion of the knee is removed and replaced by an artificial joint that form the new surfaces of the knee joint. During Robot assisted total knee replacement, Robotic Knee Replacement Surgeon uses computed tomography (CT) scans to build a 3D model of the patient’s knee. With that virtual model as guide, the surgeon then uses the robotic arm to make accurate bone cuts and insert the knee components precisely.
Well when we speak about Robotics it is indeed has to be smart and must be easily maneuvered. Knee Replacement being the prominent amongst all other joint replacement surgeries had the privilege of getting more attention from researchers and technologists. If we are to differentiate currently available knee replacement robotic systems, they are briefly classified as passive, semi-active and active systems. The major factor which has led to this differentiation is the nature of work robotic system does with least human interference. Passive & Semi Active type system guide the surgeon through the fixation and cutting block resection stages – the actual cutting and drilling processes are executed by the surgeon. Active robotic joint replacement systems which are said to be the most advanced amongst its peers are completely autonomous in nature with least human interference required.
As each person has a different face, the shape of bone is also different. Artificial joint surgical robot shows the patient’s joint bone in 3D images, and the doctor can use those images for pre-planning of surgery personalized for the patient.
What’s as important as the precise surgical plan is to select and insert the personalized artificial joint. The doctor uses robot to select an artificial joint for the patient and insert it accurately.
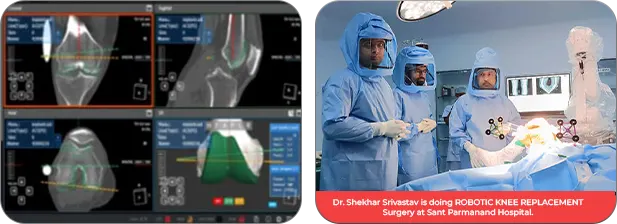
Robot reviews the data and cuts the bone precisely with respect to the dimensions of the implant decided during pre-surgery planning stage. Precise cutting serves the optimum result also provides the correct alignment of a patient’s leg axis with the sub-millimeter dimensional accuracy and precise cutting for the optimal surgical outcome.
The Surgical Robot reduces side effects like inequality of limb length, pulmonary embolism, and fracture. The risk of infection is also reduced because of fewer instruments in use than in conventional surgery.
The advantages of the Robotic knee Replacement were mainly attributed to its comprehensive pre-operative plan, intra-operative monitoring, patient specific and appropriate intervention by Robotic Knee Replacement Surgeons.
Patients can decide upon robotic artificial joint surgery after consulting with the doctor.
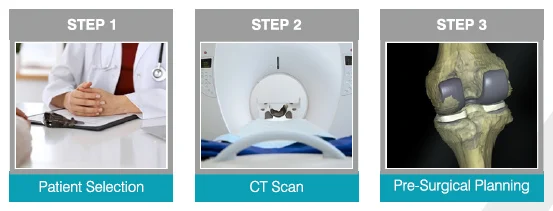
CT Scan of Knee Joints
The Scanned CT scan Image is converting into a 3D image for diagnosing the patient’s condition and make a surgical plan as required.
The patient is connected to the robot and stabilized for surgery. In the next stage, the doctor performs registration process to verify if the 3D image of the patient matches the original surgery site. After registration process, robot reviews the data and cuts the bone precisely with respect to size, position, angle and direction of the implant decided during pre-surgery planning stage.
Insert and fix the decided implant for surgery conclusion.
